层级结构
构造函数
JDK 自带的线程池 ThreadPoolExecutor 包含四个构造函数,其中最主要的如下:
/**
* 使用给定的初始化参数创建一个新的 ThreadPoolExecutor
*
* @param corePoolSize 池中保留的线程数,即使它们处于空闲状态,除非设置了allowCoreThreadTimeOut 属性
* @param maximumPoolSize 池中允许的最大线程数
* @param keepAliveTime 当线程数大于核心线程数时,这是多余空闲线程在终止前等待新任务的最长时间
* @param unit 参数 keepAliveTime 的时间单位
* @param workQueue 用于在执行任务之前保存任务的队列。这个队列只保存由 execute 方法提交的 Runnable 任务。
* @param threadFactory 执行器创建新线程时要使用的工厂
* @param handler 由于达到线程边界和队列容量而执行阻塞时要使用的处理程序
* @throws 略
*/
public ThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize,
int maximumPoolSize,
long keepAliveTime,
TimeUnit unit,
BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue,
ThreadFactory threadFactory,
RejectedExecutionHandler handler) {
if (corePoolSize < 0 ||
maximumPoolSize <= 0 ||
maximumPoolSize < corePoolSize ||
keepAliveTime < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
if (workQueue == null || threadFactory == null || handler == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
this.corePoolSize = corePoolSize;
this.maximumPoolSize = maximumPoolSize;
this.workQueue = workQueue;
this.keepAliveTime = unit.toNanos(keepAliveTime);
this.threadFactory = threadFactory;
this.handler = handler;
}
| 序号 | 名称 | 类型 | 含义 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | corePoolSize | int | 核心线程数 |
| 2 | maximumPoolSize | int | 最大线程数 |
| 3 | keepAliveTime | long | 线程最大空闲时间 |
| 4 | unit | TimeUnit | 时间单位 |
| 5 | workQueue | BlockingQueue |
线程等待队列 |
| 6 | threadFactory | ThreadFactory | 线程工厂 |
| 7 | handler | RejectedExecutionHandler | 拒绝策略 |
其他三个构造函数一个使用了默认工厂:
public ThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize,
int maximumPoolSize,
long keepAliveTime,
TimeUnit unit,
BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue,
RejectedExecutionHandler handler) {
this(corePoolSize, maximumPoolSize, keepAliveTime, unit, workQueue,
Executors.defaultThreadFactory(), handler);
}
一个使用了默认 Handler:
public ThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize,
int maximumPoolSize,
long keepAliveTime,
TimeUnit unit,
BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue,
ThreadFactory threadFactory) {
this(corePoolSize, maximumPoolSize, keepAliveTime, unit, workQueue,
threadFactory, defaultHandler);
}
一个使用了默认工厂和默认 Handler:
public ThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize,
int maximumPoolSize,
long keepAliveTime,
TimeUnit unit,
BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue) {
this(corePoolSize, maximumPoolSize, keepAliveTime, unit, workQueue,
Executors.defaultThreadFactory(), defaultHandler);
}
线程数
参数中的 corePoolSize、maximumPoolSize 分别代表核心线程数和最大线程数
线程池会根据这两个参数自动调整线程池大小
- 当在 execute 方法中提交新任务并且少于 corePoolSize 线程正在运行时,即使其他工作线程处于空闲状态,也会创建一个新线程来处理请求
- 如果有多于 corePoolSize 但小于 maximumPoolSize 线程正在运行,只有队列已满时才会创建新线程
- 通过设置 corePoolSize 和 maximumPoolSize 相同,可以创建一个固定大小的线程池
- 通过将 maximumPoolSize 设置为基本上无界的值,比如 Integer.MAX_VALUE,可以允许池容纳任意数量的并发任务
- 这两个参数可以在初始化时设置,也可以使用
setCorePoolSize方法和setMaximumPoolSize方法动态设置 - 在默认情况下,只有当新任务到达时才开始创建和启动核心线程。但是可以使用
prestartCoreThread方法和prestartAllCoreThreads方法预启动一个和所有核心线程
预启动核心线程的方法如下:
/**
* 启动一个核心线程,使其处于等待任务的空闲状态
* 这将覆盖新任务执行时启动核心线程的默认策略
* 如果所有核心线程都已启动,则此方法返回 false
*
* @return 如果一个线程创建成功返回 true
*/
public boolean prestartCoreThread() {
return workerCountOf(ctl.get()) < corePoolSize &&
addWorker(null, true);
}
/**
* 启动所有核心线程,使其处于等待任务的空闲状态
* 这将覆盖新任务执行时启动核心线程的默认策略
*
* @return 启动的线程数量
*/
public int prestartAllCoreThreads() {
int n = 0;
while (addWorker(null, true))
++n;
return n;
}
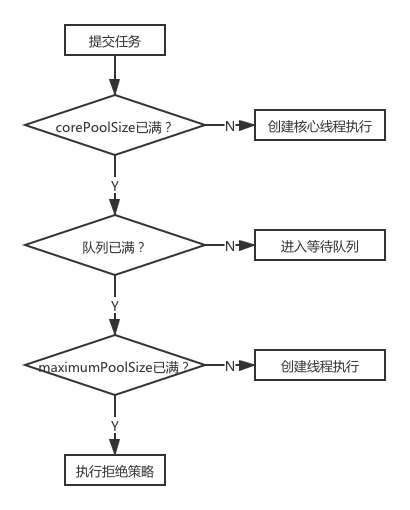
线程池对任务的处理流程如图所示:
存活时间
非核心线程的最大空闲时间由参数中的 keepAliveTime、unit 决定:this.keepAliveTime = unit.toNanos(keepAliveTime);
如果线程池中的线程数超过 corePoolSize,那么多余的线程在空闲时间超过 keepAliveTime 后会被终止
这两个参数可以在初始化时设置,也可以使用 setKeepAliveTime(long time, TimeUnit unit) 方法动态设置
默认情况下 keepAliveTime 只对非核心线程生效。但是,如果 keepAliveTime > 0,可以通过allowCoreThreadTimeOut(boolean value) 方法将该属性应用于核心线程
默认工厂
/**
* 返回一个默认的线程工厂用于创建新线程。
* This factory creates all new threads used by an Executor in the
* same {@link ThreadGroup}. If there is a {@link
* java.lang.SecurityManager}, it uses the group of {@link
* System#getSecurityManager}, else the group of the thread
* invoking this {@code defaultThreadFactory} method. Each new
* thread is created as a non-daemon thread with priority set to
* the smaller of {@code Thread.NORM_PRIORITY} and the maximum
* priority permitted in the thread group. New threads have names
* accessible via {@link Thread#getName} of
* <em>pool-N-thread-M</em>, where <em>N</em> is the sequence
* number of this factory, and <em>M</em> is the sequence number
* of the thread created by this factory.
* @return a thread factory
*/
public static ThreadFactory defaultThreadFactory() {
return new DefaultThreadFactory();
}
/**
* 默认线程工厂
*/
static class DefaultThreadFactory implements ThreadFactory {
private static final AtomicInteger poolNumber = new AtomicInteger(1);
private final ThreadGroup group;
private final AtomicInteger threadNumber = new AtomicInteger(1);
private final String namePrefix;
DefaultThreadFactory() {
SecurityManager s = System.getSecurityManager();
group = (s != null) ? s.getThreadGroup() :
Thread.currentThread().getThreadGroup();
namePrefix = "pool-" +
poolNumber.getAndIncrement() +
"-thread-";
}
// 设置新线程为非守护线程、设置优先级为 Thread.NORM_PRIORITY
public Thread newThread(Runnable r) {
Thread t = new Thread(group, r,
namePrefix + threadNumber.getAndIncrement(),
0);
if (t.isDaemon())
t.setDaemon(false);
if (t.getPriority() != Thread.NORM_PRIORITY)
t.setPriority(Thread.NORM_PRIORITY);
return t;
}
}
/**
* An object that creates new threads on demand. Using thread factories
* removes hardwiring of calls to {@link Thread#Thread(Runnable) new Thread},
* enabling applications to use special thread subclasses, priorities, etc.
*
* <p>
* The simplest implementation of this interface is just:
* <pre> {@code
* class SimpleThreadFactory implements ThreadFactory {
* public Thread newThread(Runnable r) {
* return new Thread(r);
* }
* }}</pre>
*
* The {@link Executors#defaultThreadFactory} method provides a more
* useful simple implementation, that sets the created thread context
* to known values before returning it.
* @since 1.5
* @author Doug Lea
*/
public interface ThreadFactory {
/**
* Constructs a new {@code Thread}. Implementations may also initialize
* priority, name, daemon status, {@code ThreadGroup}, etc.
*
* @param r a runnable to be executed by new thread instance
* @return constructed thread, or {@code null} if the request to
* create a thread is rejected
*/
Thread newThread(Runnable r);
}
默认 Handler
/**
* 默认的拒绝执行策略
*/
private static final RejectedExecutionHandler defaultHandler =
new AbortPolicy();
/**
* 抛 RejectedExecutionException 异常的拒绝任务策略
*/
public static class AbortPolicy implements RejectedExecutionHandler {
/**
* Creates an {@code AbortPolicy}.
*/
public AbortPolicy() { }
/**
* Always throws RejectedExecutionException.
*
* @param r the runnable task requested to be executed
* @param e the executor attempting to execute this task
* @throws RejectedExecutionException always
*/
public void rejectedExecution(Runnable r, ThreadPoolExecutor e) {
throw new RejectedExecutionException("Task " + r.toString() +
" rejected from " +
e.toString());
}
}
除了默认拒绝策略外,还有其他几种拒绝策略:
/**
* A handler for rejected tasks that runs the rejected task
* directly in the calling thread of the {@code execute} method,
* unless the executor has been shut down, in which case the task
* is discarded.
*/
public static class CallerRunsPolicy implements RejectedExecutionHandler {
/**
* Creates a {@code CallerRunsPolicy}.
*/
public CallerRunsPolicy() { }
/**
* Executes task r in the caller's thread, unless the executor
* has been shut down, in which case the task is discarded.
*
* @param r the runnable task requested to be executed
* @param e the executor attempting to execute this task
*/
public void rejectedExecution(Runnable r, ThreadPoolExecutor e) {
if (!e.isShutdown()) {
r.run();
}
}
}
/**
* A handler for rejected tasks that throws a
* {@code RejectedExecutionException}.
*/
public static class AbortPolicy implements RejectedExecutionHandler {
/**
* Creates an {@code AbortPolicy}.
*/
public AbortPolicy() { }
/**
* Always throws RejectedExecutionException.
*
* @param r the runnable task requested to be executed
* @param e the executor attempting to execute this task
* @throws RejectedExecutionException always
*/
public void rejectedExecution(Runnable r, ThreadPoolExecutor e) {
throw new RejectedExecutionException("Task " + r.toString() +
" rejected from " +
e.toString());
}
}
/**
* A handler for rejected tasks that silently discards the
* rejected task.
*/
public static class DiscardPolicy implements RejectedExecutionHandler {
/**
* Creates a {@code DiscardPolicy}.
*/
public DiscardPolicy() { }
/**
* Does nothing, which has the effect of discarding task r.
*
* @param r the runnable task requested to be executed
* @param e the executor attempting to execute this task
*/
public void rejectedExecution(Runnable r, ThreadPoolExecutor e) {
}
}
/**
* A handler for rejected tasks that discards the oldest unhandled
* request and then retries {@code execute}, unless the executor
* is shut down, in which case the task is discarded.
*/
public static class DiscardOldestPolicy implements RejectedExecutionHandler {
/**
* Creates a {@code DiscardOldestPolicy} for the given executor.
*/
public DiscardOldestPolicy() { }
/**
* Obtains and ignores the next task that the executor
* would otherwise execute, if one is immediately available,
* and then retries execution of task r, unless the executor
* is shut down, in which case task r is instead discarded.
*
* @param r the runnable task requested to be executed
* @param e the executor attempting to execute this task
*/
public void rejectedExecution(Runnable r, ThreadPoolExecutor e) {
if (!e.isShutdown()) {
e.getQueue().poll();
e.execute(r);
}
}
}
预置线程池
newFixedThreadPool
/**
* Creates a thread pool that reuses a fixed number of threads
* operating off a shared unbounded queue. At any point, at most
* {@code nThreads} threads will be active processing tasks.
* If additional tasks are submitted when all threads are active,
* they will wait in the queue until a thread is available.
* If any thread terminates due to a failure during execution
* prior to shutdown, a new one will take its place if needed to
* execute subsequent tasks. The threads in the pool will exist
* until it is explicitly {@link ExecutorService#shutdown shutdown}.
*
* @param nThreads the number of threads in the pool
* @return the newly created thread pool
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if {@code nThreads <= 0}
*/
public static ExecutorService newFixedThreadPool(int nThreads) {
return new ThreadPoolExecutor(nThreads, nThreads,
0L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>());
}
/**
* 创建一个容量为 Integer.MAX_VALUE 的 LinkedBlockingQueue
*/
public LinkedBlockingQueue() {
this(Integer.MAX_VALUE);
}